russia tests first atomic bomb impact on cold war|soviet nuclear testing 1949 : consultant This day in history at a remote testing facility in Kazakhstan, the USSR successfully detonates its first atomic bomb. It shocked the world and especially America and the test was a landmark event in the Cold War. The code name . Resultado da Desafie sua sorte com o jogo de caça-níqueis brasileiro e veja se você consegue ganhar a sorte grande nas bobinas.
{plog:ftitle_list}
BRB: denúncias colocam serviços em xeque. Com parte da cúpula do Banco Regional de Brasília (BRB) afastada e passar das páginas de economia para as policiais, veio à tona .
At a remote test site at Semipalatinsk in Kazakhstan, the USSR successfully detonates its first atomic bomb, code name “First Lightning.” In order to measure the effects of the blast, the.This day in history at a remote testing facility in Kazakhstan, the USSR successfully detonates its first atomic bomb. It shocked the world and especially America and the test was a landmark event in the Cold War. The code name . It would only be a matter of months before the U.S.S.R. exploded its own atomic bomb. The Soviets successfully tested their first nuclear device, called RDS-1 or “First Lightning” (codenamed “Joe-1” by the United States), . First Soviet Test. The Soviet Union detonated its first atomic bomb, known in the West as Joe-1, on Aug. 29, 1949, at Semipalatinsk Test Site, in Kazakhstan. The Soviets called their first atomic.
October 4, 2019, 6:31 PM. Today, detecting a nuclear test is as routine as sending someone into space. But that wasn’t the case on Aug. 29, 1949, when the Soviet Union conducted its first. During the rainy, windy early morning of August 29, 1949, the Soviet Union conducted its first nuclear explosion–code-named “First Lightning”–at the Semipalatinsk Test .Drawing on the finding of Tracerlab and other organizations, AFOAT-1 concluded that an atomic bomb had been detonated, that it was a plutonium bomb with a uranium tamper surrounding the pit, and that the date of the test was between .In total, the Soviet Union conducted 715 nuclear weapon tests throughout the course of the Cold War. Furthermore, the nuclear capabilities of the Soviet Union escalated the Cold War with the United States to the possibility of nuclear war .
The Tsar Bomba was the USSR's response to the nuclear weapons race in the Cold War. But it was far too powerful to use. It was a bomb so big that the USSR wasn't sure .This day in history at a remote testing facility in Kazakhstan, the USSR successfully detonates its first atomic bomb. It shocked the world and especially America and the test was a landmark event in the Cold War. The code name . The atomic bomb and nuclear bombs are powerful weapons that use nuclear reactions as their source of explosive energy. Scientists first developed nuclear weapons technology during World War II.
Why did the USA Drop an Atomic Bomb on Hiroshima & Nagasaki? The success of the Trinity test in July 1945 meant that the USA were capable of using atomic bombs. The USA dropped two atomic bombs on . The Soviet Atomic Bomb and the Cold War On December 25, 1946, the Soviets created their first chain reaction in a graphite structure similar to Chicago Pile-1. After encountering some difficulties with the production of plutonium and the isotopic separation of uranium over the next two years, Soviet scientists managed to get their first . The detonation of the world’s first hydrogen bomb, “Ivy Mike,” on November 1, 1952, via The Official CTBTO Photostream It is well-known that the Cold War was an arms race between the United States and the Soviet Union. What is not well-known is the sheer scale of the arsenals of nuclear weapons involved and the absolute power they were able to deliver.
The nuclear arms race was perhaps the most alarming feature of the Cold War competition between the United States and Soviet Union. . the world’s first atomic weapons test in Los Alamos, New . The Tsar Bomba was the USSR's response to the nuclear weapons race in the Cold War. But it was far too powerful to use. It was a bomb so big that the USSR wasn't sure that it could test it.The UK carries out nuclear tests in Western Australia: 1952: The USA successfully tests the first Hydrogen bomb, 2500 times more powerful than the atomic bomb: 1953: The USSR tests its own .On 6 August 1945, the USA dropped an atomic bomb close atomic bomb A powerful and destructive bomb that gets its power from the energy released when atoms are split. on the Japanese city of .
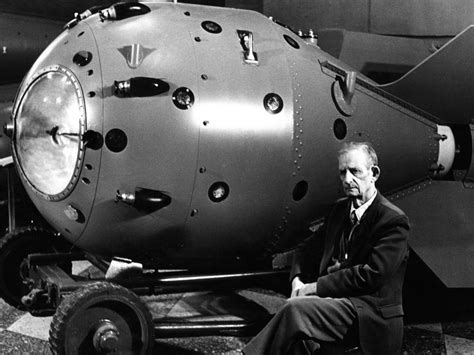
ussr atomic bomb
The Soviet Union detonated its first atomic bomb, known in the West as Joe-1, on Aug. 29, 1949, at Semipalatinsk Test Site, in Kazakhstan. The Soviets called their first atomic test "First .This allowed the USSR to test its first nuclear weapon in 1949. 3. During the 1950s, the threat of nuclear weapons was enhanced by new delivery systems. Intercontinental ballistic missiles, for example, could launch nuclear weapons thousands of miles. 4. The first half of the Cold War was marked by a nuclear arms race between the superpowers. In the 75 years since the first successful test of a plutonium bomb, nuclear weapons have changed the face of warfare. Here, troops in the 11th Airborne division watch an atomic explosion at close .While the US developed a strategy called "Operation Crossroads" in which they tested how well nuclear explosions performed on battleships, the Soviet Union constructed a domestic supply of uranium and surprised the world by detonating its first atomic bomb in August 1949.
The Soviets successfully tested their first atomic weapon on August 29, 1949, after which both superpowers upped the ante by working furiously to develop the far more powerful thermonuclear weapons, or hydrogen bombs. The United States got there first, testing their Ivy Mike Test on November 1, 1952; but once again the Soviets were close behind.
The Soviet Nuclear Program During the Cold War. The Soviet nuclear program that developed the atomic and hydrogen bomb during the early 1950s would continue to expand and accelerate during the Cold War. The .
The Semipalatinsk Test Site or Semipalatinsk-21 (Russian: Семипалатинск-21; Kazakh: Семей-21, romanized: Semei-21), also known as "The Polygon", was the primary testing venue for the Soviet Union's nuclear weapons.It is located in Zhanasemey District, Abai Region, Kazakhstan, south of the valley of the Irtysh River.The test site was part of the former Kazakh . The United States detonates the world’s first thermonuclear weapon, the hydrogen bomb, on Eniwetok atoll in the Pacific. The test gave the United States a short‑lived advantage in the nuclear .
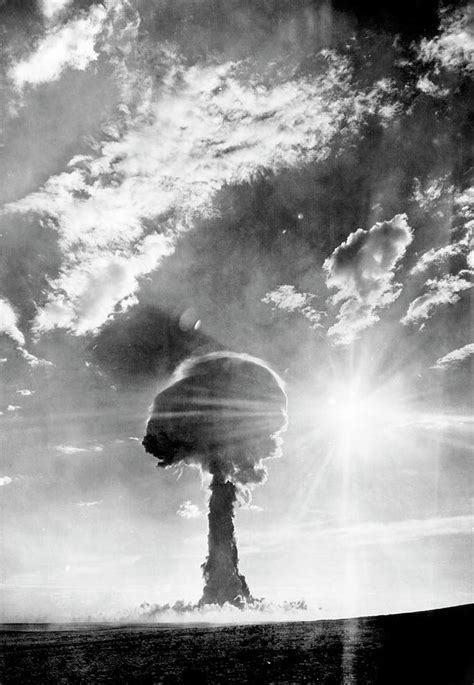
With the Soviet Union's first atomic bomb test on 29 August 1949, the "cold war" nuclear arms race between the USSR and the United States was on. . together with Russia, had hosted the Soviet . Tsar Bomba, Soviet thermonuclear bomb that was detonated in a test over Novaya Zemlya Island in the Arctic Ocean on October 30, 1961. The largest nuclear weapon ever set off, it produced the most powerful human-made explosion ever recorded. Learn more about Tsar Bomba in this article.
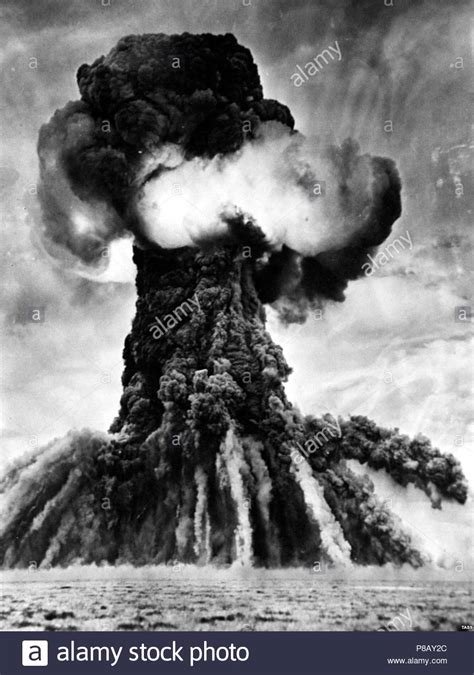

The United States was not the only leading power on the world stage after the end of World War II; it had a new competitor for this power in the Soviet Union. Tensions between the former allies quickly grew, leading to a new kind of conflict—one heightened with the threat of atomic weapons—that came to dominate global politics for the remainder of the twentieth century.
The RDS-1 (Russian: РДС-1), also known as Izdeliye 501 (device 501) and First Lightning (Russian: Пе́рвая мо́лния, romanized: Pyérvaya mólniya, IPA: [ˈpʲervəjə ˈmolnʲɪjə]), [1] was the nuclear bomb used in the Soviet Union's first nuclear weapon test.The United States assigned it the code-name Joe-1, in reference to Joseph Stalin.
In 1949, the USSR tested its first atomic bomb. This led to a race between the two superpowers to amass the most powerful nuclear weapons with the most effective delivery systems.The nuclear arms race was an arms race competition for supremacy in nuclear warfare between the United States, the Soviet Union, and their respective allies during the Cold War.During this same period, in addition to the American and Soviet nuclear stockpiles, other countries developed nuclear weapons, though no other country engaged in warhead production on . Manhattan Project, U.S. government research project (1942–45) that produced the first atomic bombs. The project’s name was derived from its initial location at Columbia University, where much of the early research was done. The first bomb was exploded in a test at Alamogordo air base in southern New Mexico on July 16, 1945.
A mushroom cloud forms seconds after detonation of the first atomic bomb at the Trinity test site in New Mexico on July 16, 1945. U.S. Department of Energy/Wikimedia Oppenheimer’s perspectiveA US Peacekeeper missile launched from a silo Minuteman III launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base, California, United States of America on 9 February 2023.. An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than 5,500 kilometres (3,400 mi), [1] primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more .
Washington, D.C., July 14, 2022 – For decades starting in the late 1940s, influential internal U.S. government analyses provided civilian and military leaders with staggering estimates of likely casualties in a nuclear conflict with the Soviet Union, but the sheer scale of those projected fatalities kept the reports classified until after the end of the Cold War.

z125 compression test

the first soviet nuclear test
Resultado da 9 de fev. de 2024 · Everyone. info. Install. About this app. arrow_forward. 10 reasons to download the GNDI easy .
russia tests first atomic bomb impact on cold war|soviet nuclear testing 1949